Orbera Gastric Balloon Safety
The ORBERA™ Intragastric Balloon System is intended for adult patients suffering from obesity, with a body mass index between 30 and 40 kg/m2, who have attempted other weight loss programs, such as diet and exercise, as well as behavior modification programs, but did not find success with these programs and were unable to lose the weight or keep it off.
The ORBERA™ Gastric Balloon requires that you be willing to follow a 12-month program, beginning when the device is placed and continuing for 6 months after the device is removed. This program includes a healthy diet and exercise plan that you must stick to. If you do not follow the diet and exercise program, you will not experience significant weight loss, and may not experience any weight loss at all.
We understand that losing weight and keeping it off is not easy. As you follow this program, you will be supervised by a team of physicians, physiologists, and nutritionists. They will be a part of your team and help you stay committed to healthy eating and exercise habits.
The ORBERA™ Gastric Balloon will only remain in your stomach for six months. Any longer than that will put you at risk for complications, such as bowel obstruction, which can be fatal.
Some patients may not be eligible for ORBERA™. A discussion with your doctor about your medical history and a physical examination will determine whether or not you are eligible for the Gastric Balloon. Moreover, while the device is being placed, your doctor may find internal factors, such as stomach irritation or ulcers, which would disqualify you from receiving the Gastric Balloon.
You CANNOT receive ORBERA™ if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant within the next six months, or are breast-feeding.
CAUTION:Rx Only
Reference: Directions For Use (DFU). ORBERA™ Intragastric Balloon System (ORBERA™). Austin, TX: Apollo Endosurgery, Inc.
Who Cannot Receive ORBERA Gastric Balloon?
• You are not a candidate for ORBERA® if you have severe damage to the liver.
• You are not a candidate for ORBERA® if you take prescription aspirin, anti-inflammatory agents, anticoagulants or other gastric irritants daily.
• You are not a candidate for ORBERA® if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
There may be other reasons why you cannot have the device. Your doctor will ask for your medical history and will examine you to decide if ORBERA® is right for you. If your doctor finds stomach problems such as irritation or ulcers, you cannot receive ORBERA®.

WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ORBERA Gastric Balloon Warnings and Precautions
ORBERA Gastric Balloon Warnings
Always tell your health care providers that you have ORBERA® and show them your Patient ID Card. If they do not know that you have ORBERA®, they may not be able to treat you correctly
Tell your doctor if anything listed in this section happens to you. This will help you get the right care.

Tell your doctor if you feel very tired, your stomach hurts, you can’t remember things, have trouble sleeping, or you are constipated. These may be signs that you are having a problem with the balloon
Tell your doctor if you no longer feel full after eating, if you are hungrier between meals than before you received ORBERA®, or if you gain weight. If this happens to you, your balloon may have deflated. A deflated balloon can stop food from passing. This may lead to stomach pain and swelling, throwing up, constipation, or even cause death. Your doctor can check to see if the deflated balloon has moved. If it has, you will need to be watched closely to see if it passes in your stool. Or, you may need an operation to remove it.
Tell your doctor if you feel severe persistent stomach pain / back pain combined with nausea or vomiting
These may be signs that your stomach is not emptying correctly or that you have an irritation of your pancreas.
Tell your doctor if you feel intense abdominal pain, feel as though your stomach may be swollen (with or without discomfort), difficulty breathing, persistent and untreatable nausea and/or vomiting. These could indicate there may be an issue with your balloon.
Tell your doctor if you have chest pain, painful swallowing, or painful breathing after placement of your balloon or after endoscopy. These may be signs that you have a tear or hole in your esophagus. Tell your doctor if you have severe, steady abdominal pain which makes it difficult for you to take a deep breath or move around. These may be signs that you have a perforation of your stomach.
Do not use ORBERA® for more than 6 months. The balloon is more likely to deflate and cause the bowels to block if it is left in place longer than 6 months. A blocked bowel can cause death.

DO NOT
Eat or drink anything for 12 hours before your appointment. Food or liquid in your stomach could enter your lungs and cause harm. If you have food in your stomach, you will have to wait until you can go 12 hours without food or drink. If you take medications, ask your doctor about how they should be taken during that time period.
DO NOT
Eat solid foods for 48 hours before your balloon is removed. Also, do not drink liquids for 12 hours before your balloon is removed. If there is food or liquid in your stomach, it can go to your lungs. Food or liquid in your lungs can cause death. If you take medications, ask your doctor about how they should be taken during that time period.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ORBERA Gastric Balloon Precautions
You must follow the diet, exercise, and other directions from your doctor while ORBERA® is in place. If you do not follow directions, you may not lose weight or you may not maintain the weight you have lost already.
Tell your doctor right away if you feel nonstop nausea, or if you cannot stop throwing up. Tell your doctor right away if you have stomach cramps that are so bad that you cannot drink any liquids. If you do not tell your doctor about your nausea or vomiting, your body could lose too much water and salts. You may need to go to the hospital to make sure you do not develop problems with your heart and kidneys. Your doctor may give you medicine to take, replace fluids through your vein, or may even have to remove your ORBERA®.
Some typical symptoms are associated with having Orbera in your stomach, including your stomach feeling unusually heavy, nausea and vomiting, acid reflux, burping, heartburn, diarrhea, and pain or cramping in your stomach or back. However, you should contact your doctor immediately if these symptoms become unusually severe or worsen significantly.
The safety and effectiveness of the ORBERA® balloon has not been established during pregnancy or breastfeeding. As soon as you know you are pregnant, tell your doctor so that ORBERA® can be removed. If you are a breastfeeding mother or planning to become pregnant within the next year, you should not use ORBERA®.

ORBERA Gastric Balloon Risk and Benefit Information
Risks Related to Endoscopic Procedures and Sedation
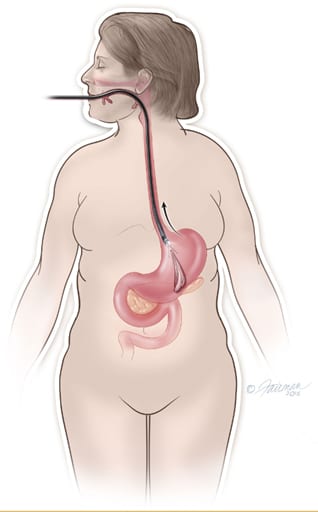
After you have been given a sedative medication, ORBERA® will be placed and removed by your doctor using an endoscope that goes down your throat and into your stomach. Endoscopy is very safe, but there are small risks. The most common risks of endoscopy include bleeding, infection, and tearing of the esophagus or stomach, which could lead to a hole forming through your esophagus or stomach. These problems only occur in about 3–5 of every 10,000 endoscopies.
Risks related to sedation during endoscopic procedures are rare, occurring in less than 1 in every 10,000 people. The most common side effects of sedative medications are temporary slowing of your pulse or breathing rate, which can be improved by the doctor giving you extra oxygen or medication to reverse the effect of the sedative.
Patients with heart, lung, kidney, liver, or other chronic diseases are at higher risk for side effects from medications. In order to reduce the chance of having a side effect during the ORBERA® procedures, you should follow your doctor’s instructions on how to prepare for endoscopy, such as not eating and stopping certain medications.

RISK AND BENEFIT
Possible Risks Related to ORBERA Gastric Balloon
ORBERA® causes stomach upset as your body gets used to the balloon. You can expect to feel some nausea, throwing up, pain, and acid reflux. These may stop on their own, or you may need medicine. Your doctor may give you medicine to help your body get used to ORBERA®.
In a U.S. clinical study of 160 people (125 patients with ORBERA® placed for 6 months plus 35 run-in patients), 139 reported nausea, 137 reported pain or discomfort, 121 reported throwing up, and 48 reported acid reflux at some time while they had ORBERA®. Most of the side effects started on the day ORBERA® was placed in the patient’s stomach or the following day.
In the U.S. clinical study, a total of 30 people out of 160 had their balloons removed early (before 6 months).
8 of the 30 people had their balloons removed early because of serious balloon intolerance which resulted in a hospital stay. The serious side effects included non-stop throwing up, nausea, pain and acid reflux that did not get better with medications.
5 of the 30 people had their balloon removed early because of other serious side effects such as lack of proper hydration, balloon blocking outlet of stomach, a hole forming all the way through the stomach, lung infection, and infection due to bacteria growth on the balloon.
2 of the 30 people had their balloons removed early due to other side effects: 1 person had gallstones and 1 person had small hollow pouches in the lining of the digestive system.
15 out of the 30 people asked to have their balloons removed early for unknown reasons and did not need to stay in the hospital.
Serious side effects are health problems which:
- May lead to hospitalization.
- Result in an illness or injury which puts you at risk for death
- Cause long lasting injury to the body
- Need quick medical treatment or surgery to prevent bodily injury
Reported serious side effects related to ORBERA® seen in the U.S. study are described in Table 1. Table 2 includes serious side effects that can be caused by ORBERA® that were not seen in the U.S. study, but are known to happen to people with weight loss balloons. The list of side effects in Table 2 is not complete as there are possible side effects that are not yet known.
RISK AND BENEFIT
Table 1: Serious side effects with ORBERA® that were seen in the U.S. study, which required hospital stay or were important medical events
| Side Effect | Number of people who had the side effect in the U.S. study (out of 160)1 | Harm, or possible harm | Onset |
| Balloon Intolerance | 8 out of 160 | Stomach pain, nausea, acid reflux, and non-stop throwing up, which can lead to lack of body water and salts 8/8 patients had early removal | Patient 1: Day of balloon placement Patient 2: Day 1 Patient 3: Day 2 Patient 4: Day 6 Patient 5: Day 11 Patient 6: Day 13 Patient 7: Day 18 Patient 8: Day 60 |
| Lack of proper hydration | 2 out of 160 | Lack of body water and salts; admitted to hospital; early ORBERA® removal 1/2 patients had early removal because of lack of proper hydration and 1 patient also had device intolerance as well as lack of proper hydration, which led to early balloon removal | Patient 1: Day 1 Patient 2: Day 3 |
| Balloon blocking the passage of food from the stomach to the intestine | 1 out of 160 | Feeling full, nausea, throwing up, stomach pain, and acid reflux; early ORBERA® removal 1/1 patients had early removal | Day 24 |
| Sudden closure of the throat during procedure | 1 out of 160 | Hard time breathing, which required a breathing tube for a short time | During the procedure |
| Injury to the lining of the esophagus | 2 out of 160 | Chest pain, fever, and admitted to hospital | During the procedure |
| A hole formed all the way through the | 1 out of 160 | Nausea, cramping, throwing up, infection, admitted to hospital, and surgery to remove balloon 1/1 patients had early removal | Day 3 |
| Lung infection caused by breathing in of stomach contents while throwing up | 1 out of 160 | Hard time breathing, pain, fever, admitted to hospital, and ORBERA® removal 1/1 patients had early removal | Day 74 |
| Stomach cramping and infection caused by bacteria growing on the balloon | 1 out of 160 | Cramping, pain, fever, and ORBERA® removal 1/1 patients had early removal | Day 154 |
1. 125 people in the study group plus 35 more people who had 1 balloon inserted and removed and then another balloon inserted on the same day so that doctors could get experience with the procedures.
Table 2: Serious side effects known to occur with weight loss balloons
| Deflated balloon prior to 6 months | A deflated balloon can pass through the intestines naturally or it can become stuck and have to be removed with surgery. If not treated, it can cause death | Was not reported in the U.S. study |
| Did not understand or remember instructions and warning statements about taking acid reducing medications | Ulcers (sores in the stomach), stomach pain and/or burning, and heartburn. If not treated may lead to a hole in the stomach, which can cause death. | Was not reported in the U.S. study. |
| Hole forming all the way through the stomach, caused by the endoscope or other reasons | Ulceration and the endoscope may not be the only causes of a hole forming in the stomach. Other causes are currently not well-understood. If not treated, it can lead to death. | Was reported once in the U.S. study (0.006%) (1 case per 160 patients) US rate for hole forming in the stomach is 0.064%* (about 6 cases per 10,000 patients) Global rate for hole forming in the stomach is 0.01%* (about 1 case per 10,000 cases) |
| Did not understand or remember instructions and warning statements about use longer than 6 months | Leaving the balloon in for longer than 6 months can lead to a deflated balloon. A deflated balloon can pass through the intestines naturally or it can become stuck and may have to be removed with surgery. If not treated, it can lead to death | Was not reported in the U.S. study. |
| A hole forming all the way through the esophagus, caused by the endoscope or other instruments | Bleeding, pain, infection, surgery to repair injury. If not treated, it can lead to death | Was not reported in U.S. study US rate for a hole forming in the esophagus is 0.029%* (less than 3 cases per 10,000 patients) Global rate for hole forming in the esophagus is <0.01%* (less than 1 case per 10,000 patients) |
| Heart problems, or heart attack during anesthesia | Chest pain, fast or slow heartbeat, and a hard time breathing. If not treated, it can lead to death | Was not reported in the U.S. study |
| Allergic reaction to medications, including anesthesia | Rash, hives, wheezing, hard time breathing, sudden drop in blood pressure, sweating, fast heartbeat, and swelling around the mouth, throat, or eyes. Severe allergic reactions can lead to death if not treated right away | Was not reported in the U.S. study |
| Compression of the Pancreas | Severe persistent stomach pain / back pain with nausea or vomiting that may be caused by irritation of or injury to the pancreas | Was not reported in U.S. study US rate for pancreatitis is is 0.043%* (about 4 cases per 10,000 patients) Global rate for pancreatitis is <0.01%* (less than 1 case per 10,000 patients) |
| Over inflated balloon | The balloon could over inflate with gas or fluid by itself while it is in a patient’s stomach. The balloon will need to be removed early. | Was not reported in the U.S. study US rate for over inflated balloon is 0.314%* (about 3 cases per 1,000 patients) Global rate for over inflated balloon is 0.07%* (about 7 cases per 10,000 patients) |
| Death | N/A | Was not reported in the U.S. study US mortality rate is 0.036%* (less than 4 deaths per 10,000 patients) Global mortality rate is <0.01%* (less than 1 death per 10,000 patients) |
| Did not understand or remember instructions and warning statements about not eating for 48 hours before removal and not drinking for 12 hours before removal or experiencing severely delayed gastric emptying | If food and liquid are retained in the stomach during removal, there is an increased risk of these stomach contents entering the lungs | Was not reported in the U.S. study US rate for aspiration is 0.029%* (less than 3 cases per 10,000 patients) Global rate for aspiration is <0.01%* (less than 1 case per 10,000 patients) |
*Rate of reported serious side effects that occurred during commercial use of ORBERA; rates are calculated based on number of devices distributed, which may be greater than the number placed.
RISK AND BENEFIT
The three most common side effects seen in the U.S. study, which did not lead to hospital, stay are nausea, throwing up, and pain. These side effects are shown in Table 3.
Side effects seen in more than 1% of patients (at least 2 out of 160) in the U.S. study, which did not lead to hospitalization, are described in Table 4 and listed in order by most frequent to less frequent. Side effects occurring in less than 1% of the patients (1 out of 160) were not related to the digestive system and are not listed. Only 5% of people had side effects that caused severe pain which made it hard for them to do their usual work or activities.
Table 3: Most common gastric (stomach)
side effects seen in the U.S. study
| Side Effect | Total number of people with side effect (percent of people with side effect) | Number of people with side effect beginning within 3 days of balloon being placed (percent of people with side effect) | Number of people with side effect starting within 3 days of balloon being placed and lasting longer than 14 days and less than 30 days (percent of people with side effect) | Number of people with side effect starting within 3 days of balloon being placed and lasting longer than 30 days (percent of people with side effect) |
| Nausea | 139 out of 160 (86.9 %) | 123 out of 139 (88.5%) | 6 out of 123 (4.9%) | 9 out of 123 (7.3%) |
| Throwing up | 121 out of 160 (75.6%) | 103 out of 121 (85.1%) | 3 out of 103 (2.9%) | 4 out of 103 (3.9%) |
| Stomach Pain (General) | 92 out of 160 (57.5 %) | 74 out of 92 (80.4%) | 5 out of 74 (6.8%) | 4 out of 74 (5.4%) |

Table 4: Side effects caused by ORBERA®, which were seen in more than 1% of patients in the U.S. study, but did not lead to hospital stay
| Side Effect | Number of people who had the side effect | Harm, or possible harm |
| Nausea | 139 out of 160 (87%) | An uneasy feeling in the stomach, or feeling like you need to throw up |
| Pain or discomfort | 137 out of 160 (82%) | An unpleasant feeling in the stomach, chest, or back |
| Throwing up | 121 out of 160 (76%) | Throwing up can lead to a lack of body water and salts. It can also cause you to breathe in food or fluids, which can cause a lung infection |
| Acid reflux | 48 out of 160 (30%) | Acid coming up from the stomach causes heartburn and chest pain, and may also cause nausea and throwing up. If not treated, it can cause other health problems |
| Burping/belching | 39 out of 160 (24%) | None |
| Heartburn | 34 out of 160 (21%) | A burning pain in the chest |
| Constipation | 32 out of 160 (20%) | Stools that are dry, hard to pass, and may be painful |
| Stomach bloating | 28 out of 160 (18%) | Swelling of the stomach |
| Lack of body water and salts | 23 out of 160 (14%) | Lack of body water and salts can cause other health problems with your heart or kidneys |
| Diarrhea | 21 out of 160 (13%) | Liquid stool more than 3 times a day can cause a lack of body water and salts |
| Gas | 18 out of 160 (11%) | Gas can cause swelling of the belly and sharp pain. |
| Slowed digestion of food | 14 out of 160 (8.8%) | Nausea, throwing up, swelling of the stomach, poor appetite, and acid reflux |
| Tiredness, weakness, dizziness, or uneasy feeling | 12 out of 160 (8%) | Being tired, weak, or dizzy can make it hard to do your usual work, and if not treated, can cause falls or injury |
| Headache or migraine | 10 out of 160 (6%) | Pain in the head, which may make it hard to do your usual work or activities |
| Device intolerance | 9 out of 160 (6%) | Severe side effects such as nausea, throwing up, pain, and acid reflux (not requiring a hospital stay). 5 out of 9 reports lead to early device removal |
| Bodily pain after procedure | 8 out of 160 (5%) | A feeling of aches and pains in the body |
| Sinus or respiratory infection, nasal congestion, or chills | 6 out of 160 (4%) | Coughing, fever, stuffy or runny nose, body aches and pain, hard to breathe |
| Bad breath | 6 out of 160 (4%) | A bad taste in the mouth and on the breath |
*Rate of reported serious side effects that occurred during commercial use of ORBERA; rates are calculated based on number of devices distributed, which may be greater than the number placed.
RISK AND BENEFIT
| Side Effect | Number of people who had the side effect |
Harm, or possible harm |
| Hard to swallow | 5 out of 160 (3%) | Having a hard time swallowing can cause a lack of body water and salts or poor nutrition |
| Irritation of the lining of the esophagus, which may be caused by not taking acid-reducing medication as instructed |
5 out of 160 (3%) | Pain in the chest that happens after eating, hard time swallowing, nausea, and throwing up. If not treated, it can cause open sores (ulcers) to form |
| Stiff stomach muscles | 5 out of 160 (3%) | Stomach is hard and painful to touch |
| Lack of Vitamin B1 | 5 out of 160 (3%) | Weak and tired |
| Sore throat | 5 out of 160 (3%) | Pain in the throat, which may make it hard to swallow |
| Infection in the stomach | 4 out of 160 (2.5%) | Pain and swelling of the stomach, nausea, and throwing up |
| Hiccups | 4 out of 160 (2.5%) | None |
| Irritation of the lining of the stomach, which may be caused by not taking acid-reducing medication as instructed |
4 out of 160 (2.5%) | Upper stomach pain or burning, nausea, throwing up, feeling of fullness in upper stomach after eating |
| Food unable to move from stomach to bowel |
3 out of 160 (1.9%) | Nausea, throwing up, stomach pain, and acid reflux, which may require early removal of ORBERA® |
| Dry heaves | 3 out of 160 (1.9%) | Strong feeling of need to throw up, but does not lead to throwing up of food or liquid |
| Lung infection | 3 out of 160 (1.9%) | Cough, fever, hard time breathing |
| Fear, worry, or hard time falling asleep |
3 out of 160 (1.9%) | An uneasy feeling which may makes it hard to do your usual work or cause you to not get enough sleep |
| Lack of appetite | 3 out of 160 (1.9%) | May lead to lack of proper nutrition and weight loss |
| Unable to control bowels | 2 out of 160 (1.3%) | An accidental liquid stool may affect your usual work or activities |
| Spasm of the intestine | 2 out of 160 (1.3%) | Pain and cramping |
| Low potassium | 2 out of 160 (1.3%) | If not treated, could lead to heart problem or death |
| Low blood count | 2 out of 160 (1.3%) | Weakness, tired, and dizziness |
*Rate of reported serious side effects that occurred during commercial use of ORBERA; rates are calculated based on number of devices distributed, which may be greater than the number placed.